Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
神崎 訓枝; 迫田 晃弘; 片岡 隆浩*; Sun, L.*; 田中 裕史; 大津 厳生*; 山岡 聖典*
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(17), p.10750_1 - 10750_14, 2022/09
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Environmental Sciences)活性イオウ分子種(RSS)は、酸化ストレスに深く関連して抗炎症作用があると報告されているが、放射線被ばく後のRSSの変化についてはまだわかっていない。そこで、本研究では、ラドン吸入後のマウス脳中のRSSに注目し、関連代謝物を網羅的に解析した。その結果、酸化型グルタチオンと還元型グルタチオンの割合、グルタチオンおよびシステインのRSSの割合はラドン吸入によって増加した。本研究でのラドン曝露は非常に低線量であったが、その酸化ストレス下でイオウイオンがグルタチオンやシステインに結合したと考えられる。また、我々は、機械学習を用いた代謝物の変化の総合的な評価により、ラドン吸入による特徴的な変化を明示した。本研究の結果は、RSSがラドン吸入の酸化ストレスに対する生体防御機構をもたらす可能性を示唆した。
片岡 隆浩*; 神崎 訓枝; 迫田 晃弘; 首藤 妃奈*; 矢野 準喜*; 直江 翔太*; 田中 裕史; 花元 克巳*; 寺東 宏明*; 光延 文裕*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 62(2), p.206 - 216, 2021/03
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:61.83(Biology)ラドン吸入はマウス臓器の抗酸化機能を活性化させ、酸化ストレスに誘導されたダメージを抑制する。そこで、本研究では、ラドン吸入後の臓器中のレドックス状態を評価した。2, 20kBq/m のラドンを1, 3, 10日間マウスに吸入させ、主成分分析や相関の変化から、抗酸化機能と酸化ストレスの関係を評価した。本研究の結果は、臓器特有のレドックス状態に依存してラドン吸入後の臓器のレドックス状態が変化したことを示唆した。
のラドンを1, 3, 10日間マウスに吸入させ、主成分分析や相関の変化から、抗酸化機能と酸化ストレスの関係を評価した。本研究の結果は、臓器特有のレドックス状態に依存してラドン吸入後の臓器のレドックス状態が変化したことを示唆した。
笹岡 香織*; 片岡 隆浩*; 神崎 訓枝; 小橋 佑介*; 迫田 晃弘; 石森 有; 山岡 聖典*
Pakistan Journal of Zoology, 50(3), p.1157 - 1170, 2018/06
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:17.52(Zoology)シスプラチン(CDDP)は固形がんの治療に広く使用されているが、酸化ストレスによる腎毒性を持っている。そこで、我々は、ラドン吸入による放射線感受性の違いによるマウス系統差によるCDDP誘導腎障害に対する影響とCDDP濃度について検討した。まず、C57BL/6JまたはBALB/cのマウスに、1000Bq/m または2000Bq/m
または2000Bq/m のラドンを24時間吸入後、CDDPを20mg/kg体重投与した。C57BL/6Jでは毛並等が改善され、BALB/cでは悪化した。次に、BALB/cマウスに、1000Bq/m
のラドンを24時間吸入後、CDDPを20mg/kg体重投与した。C57BL/6Jでは毛並等が改善され、BALB/cでは悪化した。次に、BALB/cマウスに、1000Bq/m のラドンを24時間後、CDDPを15mg/kg体重投与した。その結果、抗酸化機能の亢進などが見られた。以上のことから、ラドン吸入によってCDDP誘導腎障害を抑制することが可能であることが示唆された。
のラドンを24時間後、CDDPを15mg/kg体重投与した。その結果、抗酸化機能の亢進などが見られた。以上のことから、ラドン吸入によってCDDP誘導腎障害を抑制することが可能であることが示唆された。
鈴木 芳代; 坂下 哲哉; 服部 佑哉; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
We recently found that whole body irradiation reduced locomotion in  , though the mechanisms are not clear. It is well known that free radicals such as OH
, though the mechanisms are not clear. It is well known that free radicals such as OH and H
and H are produced following exposure of ionizing radiation. The reactions of free radicals cause the production of oxidative stress including hydrogen peroxide (H
are produced following exposure of ionizing radiation. The reactions of free radicals cause the production of oxidative stress including hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ). Oxidative stress is known as an important factor of aging, and may relate to the decrease of motility observed in the aging process. We therefore explored the potential effectiveness of H
). Oxidative stress is known as an important factor of aging, and may relate to the decrease of motility observed in the aging process. We therefore explored the potential effectiveness of H O
O in the suppression of
in the suppression of  's locomotion. Wild-type animals were exposed to graded doses of H
's locomotion. Wild-type animals were exposed to graded doses of H O
O and the locomotory rate was evaluated. The locomotory rate was significantly decreased in H
and the locomotory rate was evaluated. The locomotory rate was significantly decreased in H O
O -exposed animals, in which the dose response was similar to that in the irradiated animals. We subsequently investigated the radiation effects on the pharyngeal pumping motion (chewing and swallowing) and the involvement of oxidative stress. As a result, the proportion of the pumping-motion arrest significantly increased after whole body irradiation and the pumping-motion arrest was restored within several hours. Furthermore, the response in H
-exposed animals, in which the dose response was similar to that in the irradiated animals. We subsequently investigated the radiation effects on the pharyngeal pumping motion (chewing and swallowing) and the involvement of oxidative stress. As a result, the proportion of the pumping-motion arrest significantly increased after whole body irradiation and the pumping-motion arrest was restored within several hours. Furthermore, the response in H O
O -exposed animals was similar to that in the irradiated animals. These results support the possibility that radiation-induced suppression of both locomotion and pumping motion in
-exposed animals was similar to that in the irradiated animals. These results support the possibility that radiation-induced suppression of both locomotion and pumping motion in  was caused by radiation-produced H
was caused by radiation-produced H O
O .
.

鈴木 芳代; 坂下 哲哉; 服部 佑哉; 小林 泰彦
no journal, ,
Oxidative stress such as hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) has been identified as one of the important factors in aging, and this may be related to the decrease in motility observed during the aging process. In the present study, we therefore explored the potential effectiveness of H
) has been identified as one of the important factors in aging, and this may be related to the decrease in motility observed during the aging process. In the present study, we therefore explored the potential effectiveness of H O
O in the suppression of
in the suppression of  ' locomotion (crawling). Young adult wild-type animals were exposed to S-basal buffer containing graded doses of H
' locomotion (crawling). Young adult wild-type animals were exposed to S-basal buffer containing graded doses of H O
O . Exposure to H
. Exposure to H O
O induced reduction of locomotion similar to that observed after whole-body irradiation. To investigate the radiation effects and the involvement of oxidative stress on other types of movement, we subsequently focused on the pharyngeal pumping motion (chewing and swallowing). The proportion of animals in which the pumping motion has stopped immediately after H
induced reduction of locomotion similar to that observed after whole-body irradiation. To investigate the radiation effects and the involvement of oxidative stress on other types of movement, we subsequently focused on the pharyngeal pumping motion (chewing and swallowing). The proportion of animals in which the pumping motion has stopped immediately after H O
O exposure increased. This response was similar to that of irradiated animals. These results support the possibility that radiation-induced suppression of both locomotion and pumping motion in
exposure increased. This response was similar to that of irradiated animals. These results support the possibility that radiation-induced suppression of both locomotion and pumping motion in  was caused by radiation-produced H
was caused by radiation-produced H O
O . In this presentation, we will give an outline of the radiation effects on
. In this presentation, we will give an outline of the radiation effects on  and discuss the involvement of the radiation-induced oxidative stress in the phenomena.
and discuss the involvement of the radiation-induced oxidative stress in the phenomena.
Matsuda, Sakiyo*; Nitta, Nazuki*; Tamura, Miku*; 鈴木 芳代; 坂下 哲哉; 石井 直明*; 簗瀬 澄乃*
no journal, ,
Oxidative stress threatens cellular constructs including lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. As a result, oxidative stress causes or influence apoptosis, degenerative diseases and aging. Recently, we found an abnormal posture in short-lived mutants such as 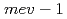 and
and 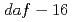 , exposed to hyperoxia. In this study, we detected the hyperoxia-induced abnormal posture in
, exposed to hyperoxia. In this study, we detected the hyperoxia-induced abnormal posture in 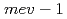 and
and 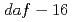 mutants compared with wild-type N
mutants compared with wild-type N and long-lived
and long-lived 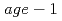 strains. 4-day-old animals placed on a NGM agar plate with a fixed bacterial lawn were exposed to hyperoxia (90% of oxygen) overnight. After the exposure, some animals were immediately recorded as digital images with up to 400-fold magnification of the microscope. The images were analyzed using image-processing software by a previously published method. To evaluate the posture of the body, we introduced a novel standard, namely the "posture index" as the absolute average of the relative angle between adjacent dividing points. As a result of this investigation, we can not only intuitively but also quantitatively and statistically understand a tendency of the behavior in various postural responses under stressful conditions in the short-lived mutants.
strains. 4-day-old animals placed on a NGM agar plate with a fixed bacterial lawn were exposed to hyperoxia (90% of oxygen) overnight. After the exposure, some animals were immediately recorded as digital images with up to 400-fold magnification of the microscope. The images were analyzed using image-processing software by a previously published method. To evaluate the posture of the body, we introduced a novel standard, namely the "posture index" as the absolute average of the relative angle between adjacent dividing points. As a result of this investigation, we can not only intuitively but also quantitatively and statistically understand a tendency of the behavior in various postural responses under stressful conditions in the short-lived mutants.
片岡 隆浩*; 神崎 訓枝; 迫田 晃弘; 石田 毅; 首藤 妃奈*; 矢野 準喜*; 田中 裕史; 花元 克巳*; 寺東 宏明*; 光延 文裕*; et al.
no journal, ,
これまでラドン吸入によってマウス臓器中の抗酸化機能が亢進することを報告してきた。ラドン吸入による抗酸化機能の亢進のメカニズムとして、微量のROSの生成が関わっている可能性が高い。そこで、本発表では、ラドンを吸入したマウス諸臓器中の抗酸化機能の活性化と過酸化水素量について調べたので報告する。
神崎 訓枝; 迫田 晃弘; 片岡 隆浩*; 田中 裕史; 山岡 聖典*
no journal, ,
近年、チオール(SH)基に過剰な硫黄原子が付加した活性イオウ分子種(RSS)は、強い抗酸化能とレドックスシグナル制御能を有していることが報告されている。そこで、本研究では、ラドン吸入とRSSの関連を検討することを目的とし、マウスの脳と肝臓でメタボローム解析を行った。ラドン吸入によって、脳では、メチオニンの増加,尿素,グルタチオン(G-SH),亜硫酸イオンの減少などが見られた。肝臓では、酸化型グルタチオン(GS-SG)の減少傾向などが見られた。また、脳や肝臓中のG-SH等のRSS(例えば、G-S-SH)の割合が増加した。今後は、脳・肝臓以外の臓器についても検討し、RSSがラドン吸入による酸化ストレス関連疾患の抑制に関与する可能性を明らかにしたい。